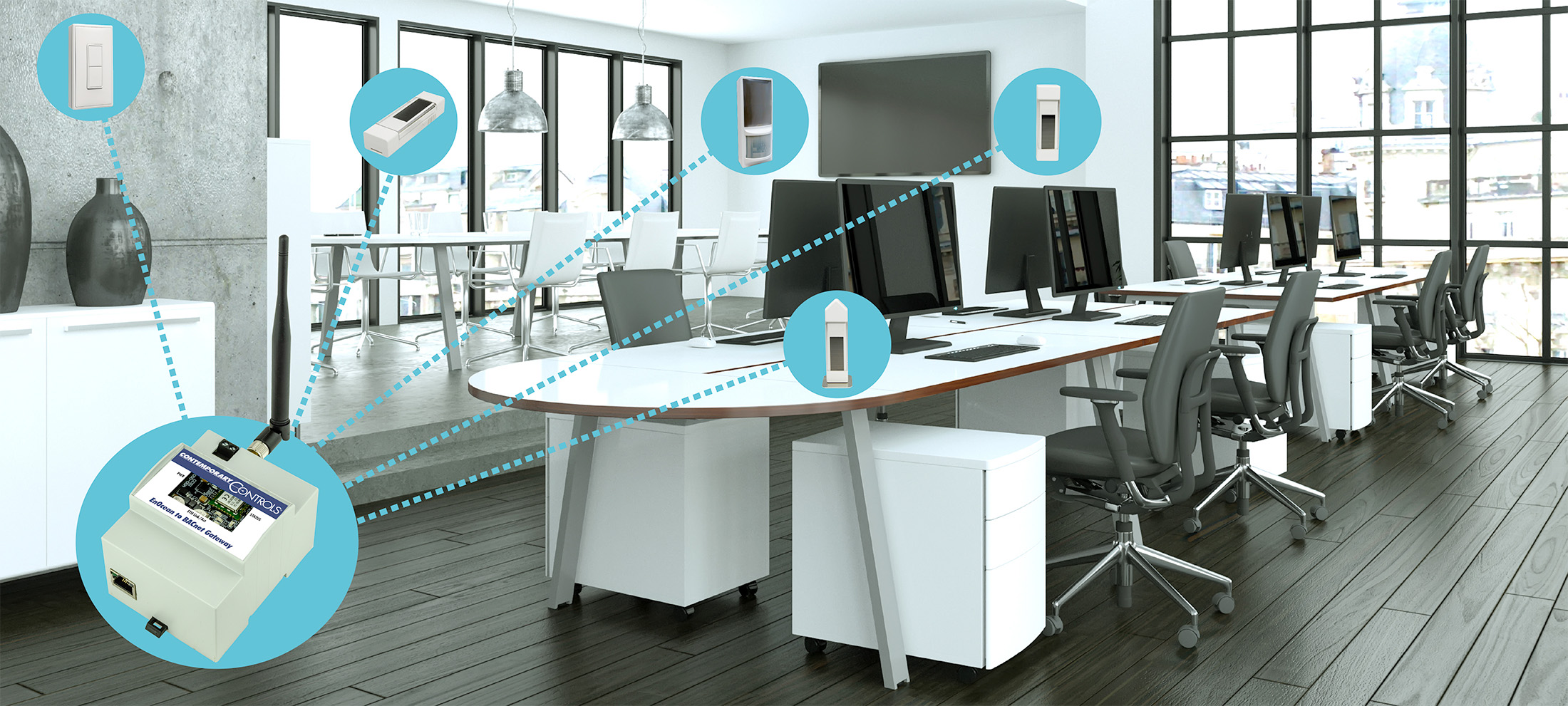
EnOcean is an energy-harvesting, wireless communication protocol that powers devices without the need for batteries or an external power source. EnOcean devices are self-powered, extracting power from ambient resources, such as solar power or kinetic energy. They feature low power consumption and reliable wireless communication in locations where it is difficult to run wires. Because these devices are low power, their wireless messages are limited in size and cannot support many of the features provided by BACnet. However in their limited capacities, EnOcean devices can be useful in BACnet systems, and an EnOcean to BACnet gateway can bring EnOcean devices into BACnet systems.
EnOcean devices can be used to bring simple data into the BACnet system, such as temperature, humidity, presence, and light levels. The BACnet system can use this data to help Control Zones save energy and provide better occupant comfort by measuring zone occupancy, temperature and humidity levels.
EnOcean devices normally cannot manage the Control Zones themselves and must rely on BACnet systems to provide this control, as well as alarms, schedules, or trends.
EnOcean is popular in lighting systems, and individual EnOcean wall switches can be used to control individual LED lights. By adding an EnOcean switch to a BACnet gateway, lights can also be controlled by the BACnet system schedule. For example, each light can be controlled by wall switches during the day, and all lights can be turned off in the evening via a BACnet schedule to conserve energy.
Contemporary Controls' EnOcean to BACnet gateway allows BACnet devices to receive EnOcean data from EnOcean input devices, such as temperature sensors, and to control EnOcean output devices through the BACnet objects it exposes to the network. Every EnOcean device registered with the gateway is given its own virtual BACnet device. Under this virtual BACnet device are a series of BACnet objects which for input devices, represent the data produced by the EnOcean device. For output devices, the objects represent the data that must be written so the gateway can transmit a full EnOcean message in order to control the output EnOcean device. Once the BACnet head-end or client has written all of the objects in the virtual output EnOcean device, it will transmit an EnOcean message to the output EnOcean device. The gateway supports remote commissioning, allowing it to be linked to the output EnOcean device via the gateway's webpages.
Contemporary Controls' gateway provides COV to communicate EnOcean messages and can be useful when working with wall switches where the button press is only provided in a single message. The gateway's BACnet objects provide additional information for the input EnOcean devices. For example, the received signal strength (RSSI) and the last time a message was received are provided as BACnet objects to help verify the network is working reliably.
To learn more about our EnOcean to BACnet gateway, visit our EnOcean to BACnet Gateway product page.

